What is Phishing?

In this era of globalization makes technology more sophisticated, with ease of technology to make e-banking transactions more attractive. Due to this ease of convenience found many e-banking crimes such as skimming and phishing.
In addition to skimming, currently also rampant theft of customer data through phishing mode. If skimming mode doubles data through ATM machines, then phishing doubles data through internet banking services.
Kontributor:
Hanna Hanifa
PHISING
The term phishing in English comes from the word fishing aka fishing, in this case means fishing information and user password. In this case, phishing is a method that hackers use to steal passwords by tricking targets using a fake login form on a fake site that resembles the original site.
Characterize the Phishing Message Feature
- Derived from an official-looking source. Phishers will design the message so it looks as if it came from a real company.
- Awaken emotions. These emotions are manifold. Can panic, worry, joy, even pity.
- Contains links or attachments. Whenever you receive a message with a link, do not click it immediately before you are sure that the source is trusted.
- Asking you to fill in certain data, such as username and password, credit card number, and so on.
Two Main Platform
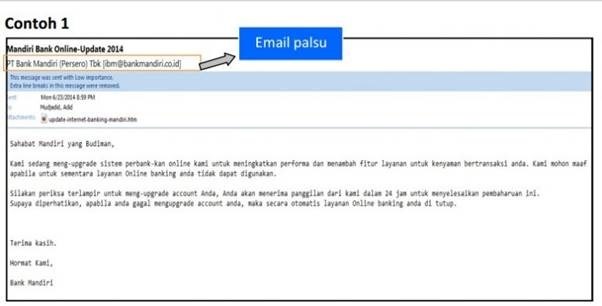
A. Fake Email
- Unofficial Email Address - Email sent from an email that resembles an official email to deceive you. In the example above Bank Mandiri, email is sent via ibm@mandiri.co.id while the original email of Bank Mandiri is mandiricare@bankmandiri.co.id.
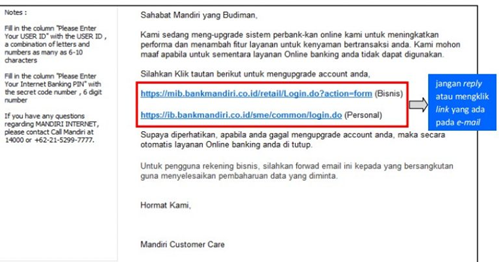
- Link to Fake Websites - Phishers want your login access to the account they want. They include links to fake websites that resemble the official website of an agency / service and then instruct you to login.
- Email Contains Threats - Phishing emails can contain threats to get the perpetrators to get what they want. The perpetrator can cleverly exploit the victim's fear to comply with instructions contained in the email. In the example above, the offender threatened to close the account immediately.
- Email Attachment - If the fake email you received contains an attachment, do not ever click and download the attachment. The offender usually inserts malware on "fake email" sent to the victim.
B. Fake Websites
- False / Unofficial URL - The picture above is one example of a phishing website that mimics the Bank Danamon website. Starting from the logo until the display is very similar to the original website which is located at https://www.danamonline.com/. However, if you look, the login link is different from the official website address of Bank Danamon, and there are additional characters on the link.
- SSL Certificate Official - Official banking company websites typically use valid SSL Certificates to ensure user safety. The fake website does not have this SSL Certificate, so it shows up like above on the URL section. If you experience this, immediately close the related page. If you have already entered login access, segeral your login details and contact the official help related.
Phishing Cases in the World
Phishing cases are rife on a global scale. According to Anti Phishing Working Group (APWG) said that the number of phishing cases has increased in the period October 2015 - March 2016. The peak occurred in March 2016. There are 123,555 reported phishing cases.
When compared with other industries, the financial sector is the target of most phishing crimes. Companies in finance and ePayment services are targeted at 21% and 20% respectively. Following behind is Social Networking services as much as 19% and email services as much as 17%.
Below are the data according to PhisLabs, a United States company engaged in Phishing protection.
Phishing Cases in Indonesia
The national banking world was once stunned with phishing cases in 2001. Someone with the initials SH bought a 'playoff' domain similar to the official domain of BCA http://www.klikbca.com/ like kilkbca.com, clikbca.com, klickbca.com and klikbac .com.
Many victims are trapped by this homemade SH site. At first glance, the homepage has the same look and looks like the original. It's just that the victim entered the User ID and PIN into SH's database instead of logging into their BCA account. He can also freely access the account of victims armed with this account information.
Until a dozen years later, similar cases still occur in Indonesia. We found news snippets covered by the news site Liputan 6 recently.
Today, phishers use more sophisticated methods. In addition to using "fake login" which only relies on username and password, the offender uses another method named account sync. The customer is asked to enter the original token number in the pop-up that has been prepared so that the offender can take the victim's balance freely. The case was reported after a BCA bank user claimed to have lost $ 13 million.
Cases of other phishing websites have also been hit Danamon Online and Tokopedia. Like the previous BCA case, the perpetrator created a fake website similar to his real name.
How Do Phishers Steal Your Account?
Here's how phishers steal your account:
- Phishing actors want your user name and password.
- Submit a login email to a mock website, to login using your account.
- The victim will login through a link that has been redirected to the mock website
- Phishers get your account to be misused, one of them is like draining your money.
There are many forms of crime that can be done after the offender gets your account information. Some examples are to drain credit cards, transfer your entire bank account to another prepared account, even if you have deposits in an e-commerce account, the offender can clear it.
Hacking passwords with phishing methods is the easiest to practice, that's why there are so many cyberspace scattered referral addresses that point your browser to a fake web or pishing web address.
Good at creating blog design is enough to be able to practice phishing.
By creating an artificial site that is not exactly the same we still can do this phishing method, as long as it can convince the target. such as a phishing site coc with frills get free gems, or fuel phishing sites which in reality the site never existed before. but many victims.
How to Avoid Phishing
- Secure your browser - Start from the security set in your browser.
- Install the browser security extension. Extensions like the Netcraft Extension serve to identify malicious websites. Very helpful.
- Be wary of emails that point you to fake websites and request login accounts. Check and check the sender's email, make sure the sender's emails match the official email.
- Be careful of pop-ups when you are accessing certain pages. Especially if the pop-up request login access or personal information such as tokens, credit card numbers, and others.
- Make sure you know and access the original website of your account. In the address bar of the official website there is usually a key icon and a valid SSL Certificate description. Official websites typically use SSL security features. This SSL security service is required for website authentication and transaction security, as well as increasing user trust. For example you can see in the picture below.
For example, the address of facebook.hanna.com site is very different from hanna.facebook.com although it looks the same and only in back and forth but it is very different. On facebook.hanna.com the main domain is hanna.com, whereas the word 'facebook' at first its a subdomain which means is part of hanna.com site.
Similarly similar domains are often used by hackers to entrap users who are not careful. When you find a phishing site you can report it to google to block the site if accessed using chrome as well as removed from search engines.
But there is more great phishing. That makes us will not be able to recognize the authenticity of the site. the domain can be exactly the same but the site is fake. Usually occurs because of a virus, the cause is because we often download software at random and then install it.
If You Become the Victims of Phishing
If you are a victim of phishing, the first thing you should do is not to panic. Realize that you have failed to do prevention efforts. Now it's time to move on to the next stage: damage control, aka minimize losses.
Change passwords for all your important accounts, such as credit card and ATM PIN, social media, email work, and so on. Use unique and unpredictable passwords for each account, so even if one account is compromised, other accounts remain secure.
Also check the settings and transaction history in the accounts that have it. Check for unauthorized transactions. Lastly, you can contact the bank to protect your accounts from break-ins.
At the end of the word, hopefully useful information and can increase knowledge about phishing. The author hopes that you put a sense of caution and do not easily believe what you read on the internet. Keep suspicious every link and attachment you receive. Always be on the lookout for transactions and accessing things that are personal.


![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh1H1G00a0lWfQxrRI1ZPvaKsBbrAdfRKAB7taGh5Cnyp5EySxSveOWp3_Bk79BOy_i3K4vwo6xg0YmcEs359dNk_nrrk0TZSusjqHsAlh3vR41QwSuv9QRsjRmRWkj5dM2-iLzqSeNEnOL/?imgmax=800)

![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgkHeMH3soagvB9kbCz2JYRBFemSLLz2grqizW7mZzHR2wxLpsd46zvxdkwcvr-m4NObzb9ERKTZubnX_HySnIDUWs9f2Wm8714IIc9CZwgPd7JiYRdufqI1N1q0eqybjR2Sy0hUpBLfjXF/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image001[4] clip_image001[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEis9ObEZ3nP0_jNIA1I_yWF2snElGlNNJnm23pCEEE91QkZEXbiHeR_D6VfsuuassaArhBPCb3dEbNKDImhDS5uzSX9eR08ulAHm4hwd7iXJhtpEeGKxxnnJPB4T-WgAe9ifEQzJFrvq2jy/?imgmax=800)

![clip_image001[6] clip_image001[6]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhQCohEBrd1V6Vaffz43ownGIEme0NbaYwDqHZMt-z3eCuaiK4oHOSH87JuMnwSGoBBmVN5WaqW1jwbr9nRCJvNh3Jeoh_fHZUwXXxjnq6ezm4-68RwcR1GDK-xJ6ADmIiS28BanD0NegYg/?imgmax=800)

