TELECOMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY
Kontributor :
Ferdyansyah Arief Wicaksono
ETYMOLGY
The French word télécommunication was coined in 1904 by the French engineer and novelist Édouard Estaunié.The word telecommunication was adapted from the French word télécommunication.Compound of the Greek prefix tele-, meaning "far off", and the Latin communicare, meaning "to share".
HISTORY OF TELECOMMUNICATION
In 1792, Claude Chappe, a French engineer, built the first fixed visual telegraphy system (or semaphore line) between Lille and Paris. However semaphore systems suffered from the need for skilled operators and the expensive towers at intervals of ten to thirty kilometers . As a result of competition from the electrical telegraph, the last commercial semaphore line was abandoned in 1880.
- The first commercial electrical telegraph was constructed by Sir Charles Wheatstone and Sir William Fothergill Cooke, and its use began on April 9, 1839.
- Then many transformation and improvement were done in telegraphics.
- The conventional telephone now in use worldwide was first patented by Alexander Graham Bell in March 1876. As with other great inventions such as radio, television, the light bulb, and the digital computer.
- Alexander Graham Bell and Gardiner Greene Hubbard, who created the first telephone company, the Bell Telephone Company of the United States, which later evolved into American Telephone & Telegraph (AT&T).
- The first commercial telephone services were set up in 1878 and 1879 on both sides of the Atlantic in the cities of New Haven, Connecticut, and London, England
Top 10 Operators in World
- AT&T - the former SBC merged with AT&T creating the new AT&T (USA)
- China Mobile - formerly China state-owned, now still state-controlled, one of two mobile phone monopolies in the entire China.
- Vodafone - Britain's largest telecom operator.
- Verizon Communications - US-based telecom company formed after a series of mergers.
- Telefonica - Multinational company with stakes in Dpain, Latin America and Europe. Owns the O2 brand.
- Deutsche Telekom - German telecom company, also owns t-mobile.
- America Movil - Mexican operator controlled by the world's richest man Carlos Slim.
- NTT DoCoMo - One of Japan's telecom operators.
- France Telecom - One of France's telecom companies.
- Nippon Telegraph & Telephone - Japan's second largest telecom operation
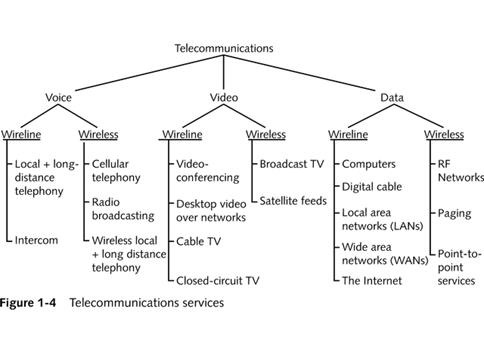
TYPES OF COMMUNICATION
- POINT-TO-POINT COMMUNICATION
- ELECOMMUNICATION OVER TELEPHONE LINES
- Voice telecommunication - using electrical signals to transmit human voice across a distance, such as telephones and radio broadcasts.
- BROADCAST COMMUNICATION
- TELECOMMUNICATION THROUGH RADIO BROADCASTS
- Video telecommunication - the electrically-based transmission of moving pictures and sound across a distance.
- MULTIPLEX SYSTEM.
- TELECOMMUNICATIONS IN WHICH MULTIPLE TRANSMITTERS AND MULTPILE RECEIVERS
- Data telecommunication - the use of electrical signals to exchange encoded information between computerized devices across a distance.
Voice
The telephony infrastructure includes cross-continental fiber optic cable to facilitate international voice telecommunications and national and regional cabling to connect long distance calls.
- It includes numerous local, regional, and national switching centers where phone calls are routed to their destinations by computerized telephone switches.
- It also includes local connections (up to three miles in length) to residences and businesses capable of greater connection speed and volume than ever before.
Data
- Telegraph - one of the first data telecommunications inventions, uses wire to convey electrical pulses that represent letters or numbers over a distance.
- Newer data telecommunications technology is not only faster, but also ensures better accuracy due to more reliable transmission media and techniques that enable the receiver to monitor the integrity of the data it has received.
- Present-day data telecommunications technologies include:
- Encoded information transmitted over traditional telephone lines
- Encoded information saved to fixed media, such as a hard disk, floppy disk, or CD ROM
- Encoded information exchanged between two computers that are directly connected by a single cable
- Encoded information exchanged by a group of connected computers on a network
- Encoded information exchanged by two devices over radio waves
Types of Telecommunications Companies
Now we talking about many companies using telecommunication technologies;
- Service providers - those that supply the communications channels for voice and data transmission.
- Equipment providers - those that supply the user and connectivity equipment, such as telephones.
- Financial Services-
- Call center - a facility dedicated to fielding customer calls.
- Interactive voice response (IVR) system - a method of sending information over the telephone by pressing buttons in response to recorded voice prompts, to answer routine questions.
- Automatic call distributor (ACD) - uses computerized devices attached to the phone lines to automatically route calls to specific phone extensions.
- Manufacturing- The use of advanced voice, video, and data telecommunications in manufacturing has resulted in faster and more efficient production of goods and at the same time it has also increased global competition.
- Supply chain management, an electronic means for connecting a manufacture with its suppliers and distributors is a notable example of the use of telecommunications in the manufacturing industry.
- Healthcare - Telemedicine - a field that brings patients and healthcare professionals together by exchanging voice, video, and data over distances when they can’t meet face-to-face.
- Improves the quality of healthcare because ailments can often be diagnosed and treated faster.
- Also streamlines the record-keeping process for clinicians who spend a great deal of time entering data about their cases.
- New Frontiers for Telecommunications Technology –
- Fiber optic cable - a transmission media that contains thin strands of fiber in its core and uses pulses of light to convey signals.
- Capable of carrying higher amounts of data, voice, or video within a given time span than any other type of media.
Now the big question is what if how the job prospects in this telecommunication field?-
Careers in Telecommunications
- No matter what type of telecommunications position you seek, the following will serve you well:
- The ability to install, maintain, and troubleshoot the system of cables and wires that carry telecommunications services
- A thorough knowledge of the public telephone network, and the carriers and regulations that are part of it
- Familiarity with enhanced telephone services (such as IVR and ACD)
- A mastery of the basic principles of electricityA clear understanding of how computers accept and interpret data from other computers over a network
- The ability to design, install, and troubleshoot basic networks
- An understanding of how the Internet works
- Familiarity with wireless transmission methods
Telecommunications Standard Organization
- Telecommunications Standard Organization
- Standards - documented agreements containing technical specifications or other precise criteria that stipulate how a particular product or service should be designed or performed.
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) - ensures that the test results from one manufacturer can be accurately compared to other manufacturers’ results.
- Both ANSI and ITU are involved in setting standards for Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) communications.